Exploring IoT: Remote Control, Smart Homes & Applications
Are you ready to embrace a world where your home anticipates your needs and your devices respond to your commands, no matter where you are? The Internet of Things (IoT) is no longer a futuristic concept; it's a transformative force reshaping how we live, work, and interact with our environment.
The applications of IoT have gained significant traction in diverse sectors, from gyms and hospitality, where personalized experiences are becoming the norm, to industrial facilities where efficiency and precision are paramount. This technological revolution is built upon a foundation of interconnected devices that seamlessly communicate and exchange data, offering unprecedented levels of control and automation.
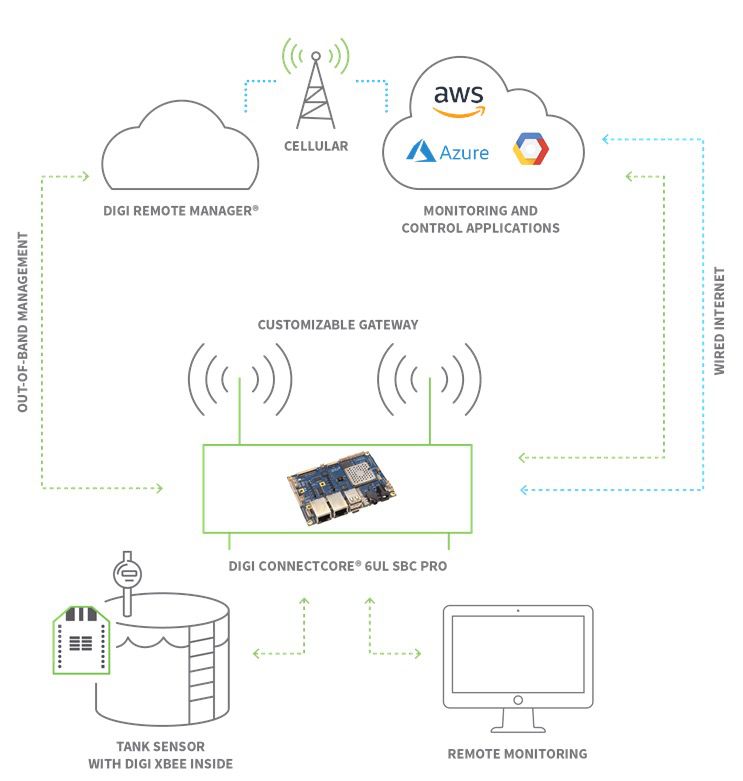
At the heart of this transformation lies the ability to control devices remotely. The impact of IoT remote monitoring is profound, fundamentally altering how we interact with and manage our surroundings on a daily basis, regardless of whether we are at home or working remotely. Remote functionality is critical in enabling seamless connectivity and control of devices from a distance, bringing convenience, efficiency, and enhanced functionality to the forefront.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition of IoT | The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of interconnected devices, from everyday household items to sophisticated industrial tools, that communicate and exchange data over the internet. |
| Key Benefits | Enhanced convenience, greater efficiency, remote control capabilities, data-driven insights, automation. |
| Examples of Applications | Smart homes (lighting, climate control, security), smart factories (remote monitoring of equipment, predictive maintenance), healthcare (remote patient monitoring), agriculture (precision farming). |
| How Remote Control Works | IoT devices are equipped with sensors and communication modules that allow them to connect to a network and be controlled remotely. This can be achieved through smartphones, web applications, or specialized control hubs. |
| Remote Monitoring | A network of sensors gather data from physical assets and environments. This data is analyzed to identify trends, optimize operations, and make informed decisions. |
| Popular Control Hubs | Smart home platforms like Samsung SmartThings or Apple HomeKit. |
| Remote Control Methods | Smartphones apps, voice assistants like Alexa and Google Assistant, web-based dashboards. |
| Remote Control Devices | Smart lighting, smart thermostats, smart security systems, smart appliances. |
| Advantages of Remote Monitoring | Efficiency, cost reduction, real-time data, improved decision-making, and enhanced user experience. |
| Challenges and Risks | Security and privacy concerns, potential for system failures, and the need for robust network infrastructure. |
| Future Trends | Integration of AI and machine learning, edge computing, more sophisticated sensors, and the expansion of IoT applications across various industries. |
| Potential Concerns | Security breaches, privacy intrusions, job displacement through automation. |
| References | Gartner IoT Glossary |
One of the most significant advantages of IoT devices is their capacity to be controlled remotely, regardless of your physical location. This remote functionality allows for convenient management and monitoring, ultimately enhancing the overall user experience. Imagine adjusting your home's thermostat from the office, preheating the oven on your commute home, or monitoring your security system while on vacation. These are just a few examples of how IoT empowers individuals with unprecedented levels of control over their environments.
The core principle behind IoT remote monitoring revolves around the collection and analysis of data gathered from physical assets and environments using a network of sensors. These sensors, meticulously attached to machines, buildings, or even agricultural fields, measure a broad spectrum of conditions, including temperature, vibration, moisture, and more. The data collected is then analyzed to identify trends, optimize operations, and make informed business decisions. For example, in a smart factory setting, sensors on production lines can provide real-time data about equipment performance, enabling predictive maintenance and minimizing downtime.
The rise of IoT has not only transformed the smart home but has also revolutionized the landscape of industrial applications. The versatility of IoT technology is evident in its widespread adoption across various sectors, including manufacturing, healthcare, agriculture, and smart cities. From streamlining operations in factories to enhancing patient care in hospitals and optimizing resource management in agriculture, the potential of IoT continues to expand.
The architecture of any given IoT device determines how it may be controlled. Physical methods for controlling an internet of things device depend only on the device architecture laid down by the developers. Conversely, remote control methods are laid down at the level of the IoT platform, and the selection of that platform therefore determines the fullness of the user experience. Its a critical aspect of the IoT equation thats often overlooked.
With the convergence of digital and physical worlds, the Internet of Things (IoT) empowers users to control various facets of their lives remotely at any time and location. Consider the simple act of turning on your lights from your smartphone or receiving a notification that your washing machine has completed its cycle. These interactions, once requiring physical presence and manual intervention, have now become seamless and automated, thanks to the power of IoT.
Various platforms have emerged to manage and control these devices remotely, offering a range of functionalities and control options. These platforms act as a central point of control, allowing you to manage multiple devices from a single interface. Examples of popular control hubs include smart home platforms like Samsung SmartThings or Apple HomeKit, which provide intuitive interfaces for managing devices, creating scenes, and automating tasks.
Iot remote control is extremely valuable across the board in all industries, as it provides a mechanism to remotely control IoT devices. Through these IoT applications, homeowners can control devices and appliances, lighting, security systems, and climate using smartphones or voice assistants. This level of automation provides greater convenience and energy efficiency.
Any failure of IoT devices can become a very costly issue for a company. Given the financial and reputational risks associated with downtimes of IoT systems or data loss caused by tech problems, it\u2019s much better to invest in implementing remote management than to deal with the consequences of device failures.
The interconnected network of devicesranging from everyday household items to sophisticated industrial toolsthat communicate and exchange data over the internet. This ecosystem enables a seamless flow of information, allowing us to monitor and control our environment.
Consumer IoT applications focus on convenience and enhancing the user experience, as seen in devices like smart TVs, smart thermostats, and wearable fitness trackers. In the home, smart air and temperature sensors can adjust based on preferences. Smart lighting controlled remotely from smartphones offers another example. Another common example is smart appliances such as smart ovens with remote control that allows users to adjust settings or receive notifications when meals are ready, offering unparalleled flexibility and peace of mind.
The introduction of industrial automation and intelligent assembly systems are now changing the manufacturing process, with IoT remote control now making it easy to maintain the performance of intelligent devices used in a production line.