IoT Explained: What You Need To Know | Examples & Applications
Do you ever stop to consider the invisible web that connects our world, transforming the mundane into the extraordinary? The Internet of Things (IoT) is quietly revolutionizing every facet of modern life, from the way we manage our homes to the efficiency of global industries.
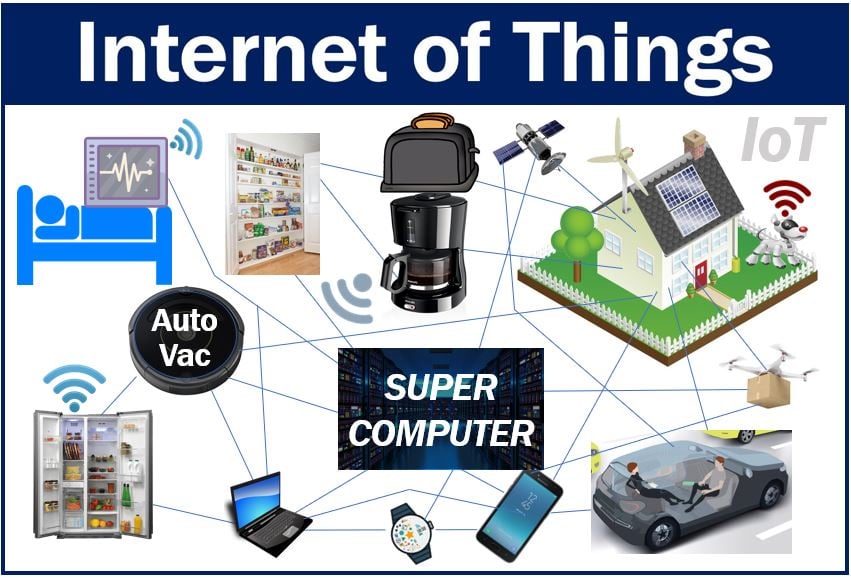
The term "IoT," or Internet of Things, encapsulates a vast network of interconnected devices. These devices, ranging from commonplace household items to complex industrial machinery, communicate and exchange data over the internet. This interconnectedness creates an ecosystem where information flows seamlessly, allowing devices to monitor, share, and react to data without direct human intervention. This represents a fundamental shift in how we interact with technology, transforming how we live, work, and engage with our surroundings. The essence of IoT lies in its ability to turn the remote control of everyday objects into a tangible reality, accessible from virtually any location.
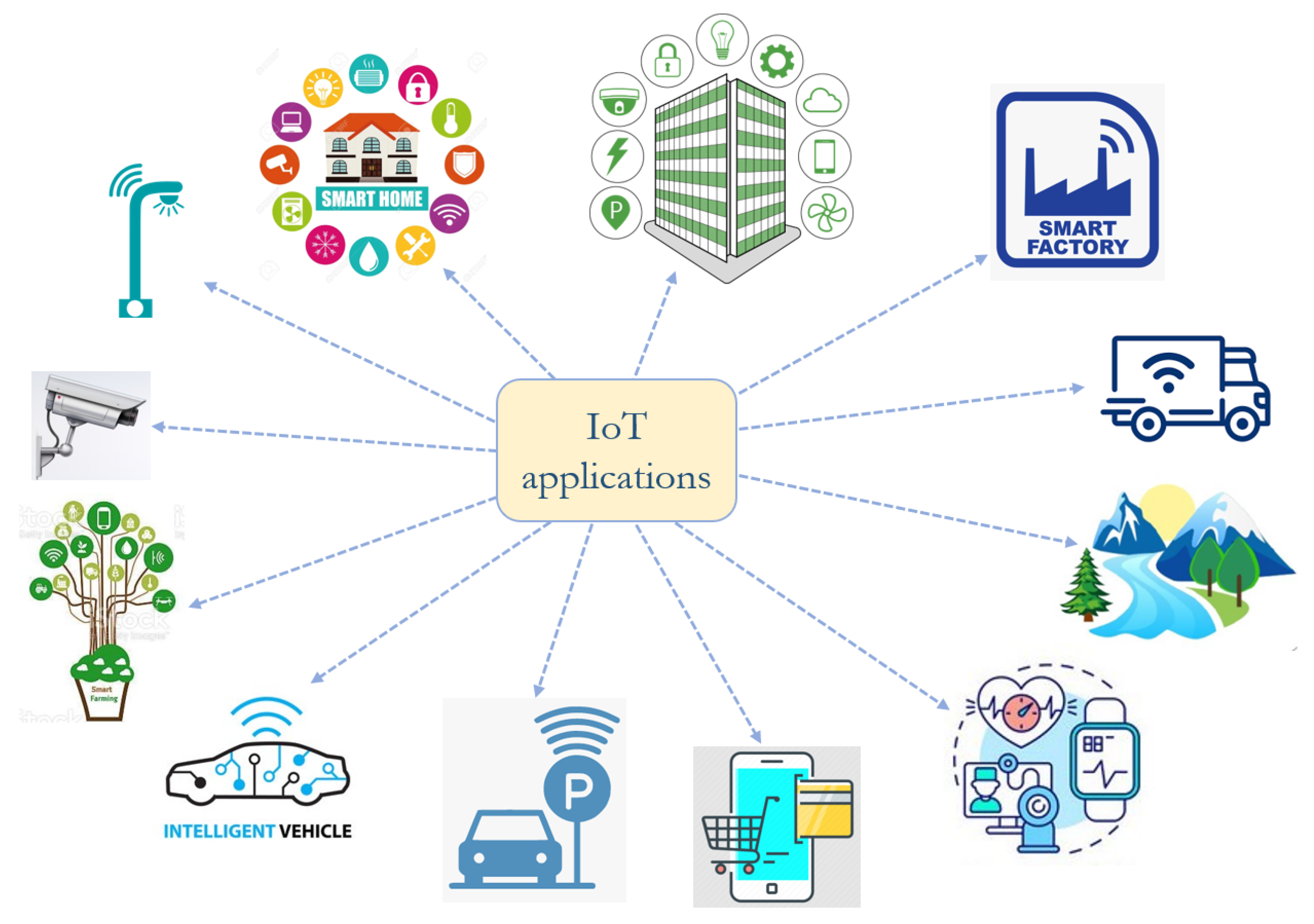
The IoT landscape is vast and multifaceted, touching upon numerous aspects of modern life. Here's a breakdown of key elements:
| Aspect | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The interconnected network of physical devices, vehicles, home appliances, and other items embedded with electronics, software, sensors, actuators, and connectivity which enables these things to connect and exchange data. | Smart thermostats, wearable fitness trackers, and connected cars. |
| Key Technologies | Includes a combination of wireless communication (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular), embedded systems, sensor technology, cloud computing, and data analytics. | Low-power wide-area networks (LPWANs) like LoRaWAN, and 5G. |
| Applications | Spans smart homes, healthcare, industrial automation, smart cities, agriculture, retail, and transportation. | Remote patient monitoring, predictive maintenance in factories, and smart traffic management systems. |
| Benefits | Improved efficiency, automation, convenience, enhanced data collection, better decision-making, cost savings, and new business opportunities. | Reduced energy consumption in smart buildings and improved supply chain management. |
| Challenges | Security vulnerabilities, data privacy concerns, interoperability issues, scalability, and the need for standardized protocols. | Protecting sensitive data collected by smart devices and ensuring device compatibility across different platforms. |
| Future Trends | Growth in edge computing, increased use of AI and machine learning, greater focus on security and privacy, and the development of new IoT-enabled applications. | Autonomous vehicles, smart agriculture, and advanced robotics. |
| Impact | Transforming industries, creating new business models, and reshaping the way we live, work, and interact with the world. | Increased productivity, improved quality of life, and sustainable practices. |
This is the core idea behind the Internet of Things (IoT): the capacity to manage these everyday objects via the internet, making them accessible from anywhere in the world. This concept is more than a futuristic dream; it's a present-day reality.
Consider this: you're relaxing on a beach, enjoying a refreshing drink, while effortlessly controlling your home's thermostat using your smartphone. This seemingly simple scenario perfectly illustrates the power and convenience of IoT in action. You're also likely engaging with IoT devices on a daily basis, perhaps without even realizing it.
One of the most recognizable examples of IoT in action is the prevalence of personal assistants like Amazon's Alexa within smart homes. These devices, often referred to as "smart devices," are becoming increasingly popular due to their ease of use and the convenience they offer.
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) represents a critical subset of IoT, focusing on interconnected devices within the industrial sector. This includes manufacturing machinery and devices designed for efficient energy management. For example, Tektelic's solutions for remote monitoring, originally developed for storage facilities, can also be applied in retail environments. These applications ensure ideal product conditions and minimize risks, such as water leaks or environmental damage, providing valuable insights and improvements.
The evolution of IoT has been marked by significant milestones.
| Year | Event | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| 1980s | The first IoT device emerged: a networked Coke machine. | Demonstrated the early potential of connected devices for monitoring and inventory management. |
| 1990 | John Romkey created the first "modern" IoT device: a toaster controlled by a computer. | Further showcased the concept of remote device control. |
| 1999 | Kevin Ashton coined the term "Internet of Things." | Provided the name that we now use to describe this rapidly growing space. |
| Present | Rapid proliferation of IoT devices across various sectors. | Widespread adoption and the emergence of new applications and challenges. |
| 2025 (Projected) | Number of connected devices expected to reach 27 billion. | Demonstrates the exponential growth of the IoT market. |
| 2030 (Projected) | The world will have over 29 billion IoT devices | Further highlights the massive expansion and integration of IoT into all aspects of daily life. |
The increasing sophistication of smart homes, fueled by the proliferation of IoT devices, amplifies the attack surface for cybercriminals. The security of IoT devices and the secure connections they utilize are, therefore, critical, given the nature of the personal and highly sensitive data transmitted between IoT devices and cloud storage.
The IoT also facilitates global remote working, allowing individuals and businesses to access their applications from devices anywhere in the world. Consider the convenience of adjusting your home thermostat or monitoring your security cameras, all from the comfort of your beachside vacation. This isn't just about convenience; it's about transforming the very nature of how we manage our lives and businesses.
The development of IoT applications often requires a robust mechanism for managing device states, either locally or remotely. This capability is crucial for ensuring reliable operation and for troubleshooting issues.
Furthermore, the accessibility of IoT is enhanced by intuitive interfaces and smart devices, making it easy to learn new software and integrate IoT into daily routines. IoT devices and applications are also available at relatively low costs, making them accessible to a wide range of users.
The Internet of Things (IoT) touches upon various applications.
| Application Area | Examples | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Homes | Smart thermostats, lighting systems, security cameras, voice assistants (Alexa, Google Assistant). | Enhanced comfort, energy efficiency, home security, and convenience. |
| Healthcare | Wearable fitness trackers, remote patient monitoring systems, smart medication dispensers. | Improved patient care, remote health monitoring, and cost reduction. |
| Industrial Automation (IIoT) | Predictive maintenance, smart sensors on machinery, automated inventory management. | Increased efficiency, reduced downtime, improved productivity, and cost savings. |
| Smart Cities | Smart traffic management, intelligent street lighting, waste management systems. | Improved traffic flow, reduced energy consumption, optimized resource allocation, and enhanced quality of life. |
| Retail | Smart shelves, inventory tracking systems, customer behavior analysis. | Improved inventory management, enhanced customer experience, and increased sales. |
| Agriculture | Smart irrigation systems, sensor-based crop monitoring, precision farming techniques. | Increased crop yields, reduced water consumption, optimized resource management, and improved sustainability. |
| Transportation | Connected cars, autonomous vehicles, smart traffic management systems, fleet management. | Improved safety, reduced traffic congestion, enhanced efficiency, and new mobility solutions. |
The Internet of Things (IoT) is not merely a buzzword; it is a fundamental shift, turning the once-distant idea of remote control into a practical, everyday experience. As we move forward, the IoT will reshape the way we live, work, and interact with our surroundings, promising even greater innovation and seamless integration into every facet of our lives. This interconnectedness is already revolutionizing industries and daily routines.